Ten Remarkable Achievements of Ancient Egypt

Ancient Egypt is one of the greatest civilizations in human history, flourishing for over 3,000 years. Its legacy includes monumental architecture and groundbreaking scientific practices. Unlike the Greeks, whose achievements were largely academic and philosophical, the Egyptians focused on practical applications of knowledge to improve daily life. In this post, we list ten of their most significant accomplishments:
-
1. The Practical Use of the Scientific Method

The Egyptians didn't have a formal term for "science", but their methods reveal a clear scientific approach through observation and experimentation. This is evident in the Edwin Smith and Ebers Medical Papyri, which outline systematic methods for diagnosing and treating illnesses. Physicians followed a structured process that started with interviewing the patient, examining their symptoms, making a diagnosis, applying treatment, and documenting the outcome.
Scientific principles extended to other fields as in architecture. Large structures like the pyramids and the temples required knowledge of engineering and mathematics. Even with the little information that we have, it is clear that science was an important aspect of Egyptian life, used as a tool for solving real-world problems.
-
2. Advanced Mathematics

Egyptians developed a very functional mathematical system that they used to solve daily-life tasks particularly in architecture, engineering, and agriculture. Unlike the Greeks, who favored theoretical formulas, Egyptians used step-by-step calculations to solve real problems.
Their mathematical achievements included:
- Use of basic fractions (½, ¼, ⅓)
- Calculating areas of rectangles and triangles
- Estimating the area of circles using an early value of pi (about 3.16)
- Determining volumes of cylinders and pyramids
Their mathematical expertise is mostly visible in the construction of the pyramids, where precise measurements and proportions ensured stability and symmetry.
-
3. Practical Astronomy

Egyptians used astronomy to serve religious, agricultural, and architectural purposes. Star constellations were documented on tomb ceilings and coffin lids, often serving as star clocks.
They applied their knowledge in astronomy in several practical ways that included:
- Scheduling ceremonies based on star visibility
- Aligning pyramids using the North Star
- Starting the New Year with the rising of Sirius, coinciding with the Nile’s flooding
By the New Kingdom, Egyptians had identified five planets, referring to them as "stars that know no rest". They were associated with deities like Horus and Seth. While astrology arrived later with the Greeks, the Egyptians laid a strong foundation in observational astronomy.
-
4. Deep Understanding of Human Anatomy
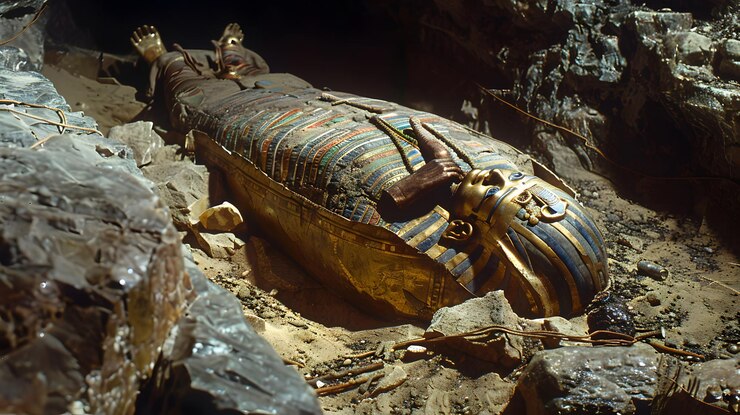

Egyptian knowledge of the human body was remarkable considering the limitations of their era. Their understanding stemmed largely from their need for mummification, which provided insight into internal organs.
The Edwin Smith Papyrus shows early knowledge of blood circulation. It notes the link between heartbeat and pulse and describes vessels reaching every part of the body. Even their mythology reflected anatomical awareness—Khnum, the ram-headed god, is described as molding humans with functioning organs and systems.
Though they likely avoided live internal surgeries, the Egyptians were among the first to view the body as a system, contributing significantly to early medical science.
-
5. Innovative Irrigation Systems

Living in a desert, Egyptians had to maximize the use of the Nile River. Their irrigation systems were an extraordinary feat, involving canals, reservoirs, and water-lifting devices.
During the Middle Kingdom, the Faiyum lake was used as a reservoir. They collected floodwater for use during dry periods. Canals connected the Nile to these storage sites to ensure year-round water availability.
Archaeologists discovered several ancient water-lifting tools including:
- Manual vessels during the Old and Middle Kingdoms
- Shaduf, a counterweighted pole with a bucket, in the New Kingdom
- Sakkia, an animal-powered water wheel, during the Ptolemaic era
These innovations allowed more land to be irrigated allowing agricultural productivity and sustaining a large population.
-
6. The World’s First Stone Buildings

The step pyramid built by King Djoser at Saqqara was the first major stone building in the world. It began as a simple mastaba tomb but evolved into a six-step structure rising 60 meters high.
This was revolutionary because earlier buildings used mud bricks. Djoser’s architects replicated mud-brick dimensions using stone, creating a structure meant to last forever. The pyramid’s limestone casing gave it a smooth, impressive finish.
After Djoser, stone became the material of choice for temples and tombs—structures. This innovation set a new architectural standard that influenced other civilizations.
-
7. The Great Pyramid of Giza – A Surviving Wonder
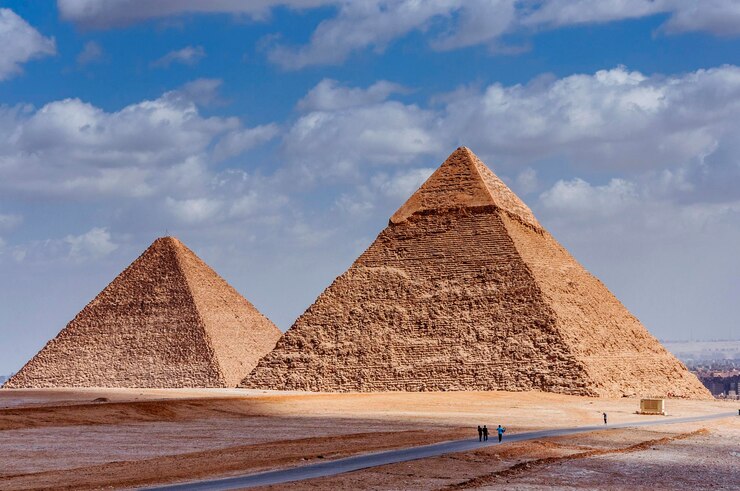

You knew that was coming somewhere in the list. The Great Pyramid of Giza is one of the most inspiring achievements in history and the only surviving Wonder of the Ancient World. Commissioned by King Khufu around 2560 BC, it stands 146 meters tall and dominates the Giza plateau.
The Great Pyramid showcases architectural precision, containing burial chambers, passageways, and a red granite sarcophagus. Despite no confirmed royal burial in the structure, it remains a testament to ancient engineering skill.
Even in antiquity, the pyramid drew tourists—Cleopatra, Julius Caesar, and even later pharaohs visited it in admiration.
-
8. Mastery of Glass Production

Glassmaking became a significant industry during the New Kingdom, with techniques likely adopted from Syria. Over time, Egyptians perfected both glass production and artistry using whatever raw materials that were available to them such as silica, lime, and alkali.
Artifacts show that ancient Egypt developed several methods for producing glass including:
- Core moulding: Shaping a vessel around a clay core
- Cold cutting: Sculpting pre-formed glass as if it were stone
- Moulding: Pouring molten glass into clay forms
Glass items were luxurious, often reserved for royalty or diplomatic gifts. Decorative techniques included colored swirls, marbled effects, and feathered patterns.
Archaeological finds at Amarna, Luxor, and Pi-Rameses confirm widespread and skilled glass production, making it one of the earliest luxury industries in the world.
-
9. Female Leadership and Economic Expansion

Hatshepsut, Egypt’s most famous female pharaoh, broke gender norms by ruling as king rather than queen. Her reign, lasting about 20 years, was marked by peace and prosperity.
She even tried to cultivate incense trees in Egypt, aiming to create a self-sufficient supply. Although it’s unclear if this succeeded, her economic initiatives greatly enriched Egypt and extended its influence.
-
10. A Civilisation That Lasted Over 3,000 Years

Perhaps Egypt’s most astounding achievement is its longevity. While empires like Rome and Greece rose and fell in few centuries, Egyptian civilization lasted from 3100 BC to 30 BC, that is more than 3,000 years.
This longevity was due to their flexibility. Egyptians readily absorbed foreign gods, customs, and technologies. They created a culture with something for everyone. Eventually, the influx of foreign rule overwhelmed their adaptive capacity and their native traditions faded. But thanks to archaeology, the story of this incredible civilization continues to unfold.